Many people have nails and skin affected by the fungus, which doesn't look very nice. It is important to understand that this is not only an aesthetic problem, but above all a medical one.
In some cases, skin lesions from fungi can be a harbinger of serious diseases, such as diabetes. Do not start with the disease, since the treatment process takes a year or more on average.
How can you get skin and nail fungus?
More than 40 species of different parasitic fungi (dermatophytes) are known to affect skin and nails. The most common are representatives of the genera Trichophyton, Microsporum and Epidermophyton. For growth and reproduction, they use a special substrate - keratin, which consists of the top layer of skin (epidermis), hair and nails. Penetrating the epidermis or nail plate, the fungus is fixed there, begins to grow and multiply.
You can get infected from a sick person, through objects (towels, wooden shelves in a bathhouse, sauna, carpets, benches in public pools, manicure/pedicure tools) and contact with soil if you like to walk barefoot in nature.
risk groups
The most common types of fungal diseases include mycoses of the skin of the feet and onychomycoses of the nail plates. Several weeks to several months elapse between the time of infection and the appearance of the first clinical symptoms.
Men suffer from fungal diseases more often than others. In women, those who wear pointy shoes, especially high heels, all the time are more likely to get the disease. In this case, the toes are constantly flattened, which causes friction, small wounds, abrasions, which are the gateway for infection.
You can "catch" a fungus even in an ordinary beauty salon during a pedicure, if the master used improperly processed tools. To remove spores and fungal fragments from the metal surfaces of tongs, scissors and tweezers, the tools must be sterilized in a drying cabinet. Not all salons have such equipment, so they limit themselves to "soaking" in a disinfectant solution and "drying" in UV boxes. This treatment does not completely protect against infection.
Frequent occurrence of a fungal infection can signal the development of diabetes. According to statistics, diabetics are three times more prone to mycosis. Also, the fungus can appear with allergic skin lesions (itching, inflammation, oozing), combing insect bites, while taking antibacterial drugs, corticosteroid hormones and antidepressants.
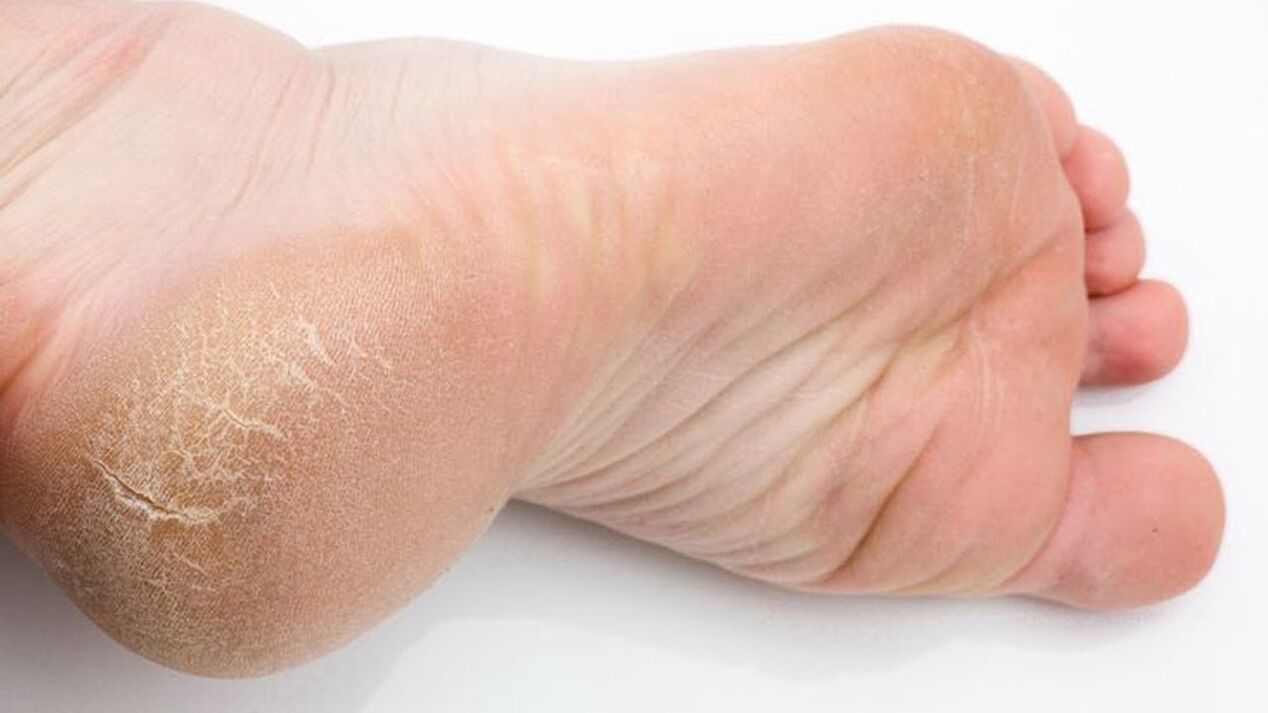
Symptoms of athlete's foot
- Dry skin, cracks, peeling in the interdigital folds.
- Itching.
- Hyperkeratosis (thickening of the skin on the feet).
- enlargement of lesions.
- In some cases, a difficult-to-cure fungal infection is accompanied by a staph infection.
Symptoms of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
Onychomycosis accounts for up to 40% of all nail diseases. Dermatophytes account for up to 90% of all fungal nail infections. The most common pathogens are fungi of the genus Trichophyton.
The appearance of the fungus in this case may be preceded by injury to the nail or constant softening of the nail plate due to high humidity. This is possible, for example, if you wear the same pair of shoes/sneakers every day.
As the infection progresses, the color of the nail changes - part of the nail becomes yellow, greyish or whitish. Over time, the spot grows, and the nail itself thickens - the development of subungual hyperkeratosis occurs.
Diagnosis of fungal diseases
Special tests to detect fungi are used to diagnose fungal infections and onychomycosis. Biomaterial (hair fragments, nail plates, skin particles) is analyzed under a microscope. If the infection has taken place and the threads of the mycelium (the body of the mushroom) are visible, the diagnosis is confirmed.
If microscopic examination gives an ambiguous answer, then a bacteriological examination is carried out - sowing the material for fungi. The test allows not only to identify the infection, but also to determine susceptibility to antifungal drugs, which is necessary for the selection of effective treatments.
How to protect yourself from fungus
- Dry your feet after bathing or showering, especially between your toes.
- If you wear closed-toe shoes, change your socks/socks daily.
- Change shoes every two or three days, don't wear the same pair every day.
- Do not walk barefoot in public places (swimming pool, bath, sauna, fitness club).
- If someone in your family has a fungal disease, provide them with a separate set of towels and linens. Wash them separately at the highest temperature.
- If you have fungus on the same foot or nails, use two different manicure/pedicure sets to avoid spreading the infection to healthy areas.
- If you have diabetes, control your blood sugar levels. "High sugar" reduces the healing rate of wounds on the skin ("diabetic foot"), making it easier for a fungal infection to enter.
Health!


















